How to Develop an Effective Cloud Strategy

A poor cloud strategy includes everything from no planning at all to performing migrations to the cloud that are not organized or not carefully planned. This is why people even hire cloud strategy advisors to help them to form an adequate cloud plan.
This can result in choosing the wrong cloud vendor and unexpected cloud expenditures. It could also negatively affect business continuity and cloud architecture. It could even impact customer satisfaction.
The negative effects on your business can certainly be real. This helps to emphasize that asking the right questions and thinking through the cloud strategy from a business perspective from start to finish is extremely important.
Ultimately, having a poor cloud strategy leads to a waste of money and resources. Let’s see how to build an effective cloud strategy. This leads to being able to migrate to the cloud as efficiently as possible, and it helps to minimize unexpected challenges.
Defining Your Cloud Strategy
Let’s define cloud strategy, using a cloud strategy example to illustrate. Cloud technologies can give your business access to exciting capabilities, translating into better business processes, satisfied customers, and increased growth. However, choosing to migrate your business to the cloud should include proper planning and preparation. Let’s look at how to develop an effective cloud strategy and the decisions that need to be made along the way.
There are more considerations to migrating to the cloud than merely saying you need to migrate to the cloud. Specifically, there are many aspects of cloud migration that need to be determined beforehand to understand the proper strategy for your cloud migration.
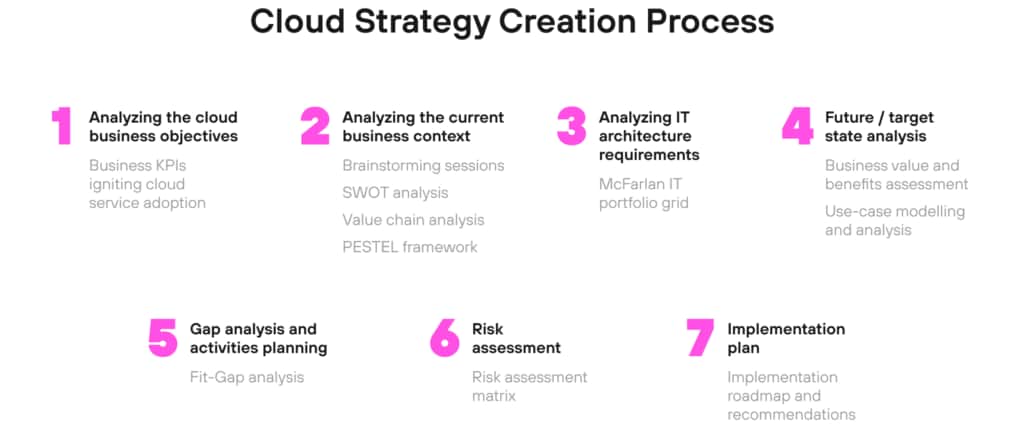
1. Identify Benefits and Risks
Business stakeholders first need to determine the motivation behind wanting to move to the cloud. There is no doubt that cloud technologies offer real benefits for businesses today. However, asking the right questions can help to provide focus to your cloud strategy. The following are important questions that you need to answer to develop a cloud strategy.
- Is there a real business need that will be solved by moving data and services to the cloud?
- How will the business benefit by moving to the cloud?
- What types of data are best suited to move to the cloud?
- Will all data be moving, or only a certain type of data?
- What type of cloud configuration is being considered? Hybrid cloud, private cloud, public cloud, and multi-cloud are popular options.
- What new challenges will be involved with moving data to the cloud?
- Is there a plan to handle new challenges with cloud security and cloud backups?
- Does IT operations have the training and tools needed to handle the migration to the cloud?
The above questions will help make a good start in forming the best cloud strategy. It becomes obvious that there is much more involved than simply saying, “we want to move to the cloud,” pulling the trigger and being done. There are many aspects to any cloud migration strategy.
Now that the business stakeholders have made the decision to move to the cloud, what’s next? The cloud computing adoption strategies need to outline what type of cloud deployments to consider when migrating data to the cloud.
2. Choose Cloud Deployment Type
When it comes to migrating your data to the cloud, what type of cloud computing strategy should you use? Let’s look at four cloud deployment configurations that are typically found in an effective cloud strategy. These include:
- Private Cloud
- Public Cloud
- Hybrid Cloud
- Multi-Cloud
What are these four types of cloud deployments? How do they differ, and what makes one a better fit over another?
Public Cloud
The Public Cloud is arguably the most popular option discussed when formulating your cloud strategy for data migration. Public cloud is the idea that most have when they think about cloud computing. Public cloud environments are the cloud environments that include the likes of Amazon AWS, Google GCP, and Microsoft Azure.
Public cloud environments typically come under the most scrutiny for security concerns. By their very nature, these environments are a “shared” platform. With any type of platform that shares access in a multi-tenant environment, there are always additional security risks to be considered.
Providing data protection to your public cloud environment is always an extremely important consideration to be made. This requires your business to think also about cloud backup strategies that will be used to protect data.
Private Cloud
Security is one of the longstanding concerns with migrating your data and applications to the cloud. Today’s “public” cloud providers today have made great strides in improving data security. Yet, many businesses may still find it necessary to retain full control over their data in the cloud.
This leads to businesses deciding on a Private Cloud deployment. Private clouds are usually servers that the business owns and operates. They are often collocated in a separate data center. While they offer many features similar to public cloud environments, they come with more stringent security controls.
Private cloud environments could be a strategic move for businesses with strict compliance and security regulations. These businesses have numerous security demands that they need to meet. Examples include businesses in the financial sector, government, and healthcare. However, developing a cloud strategy centered on private cloud environments is the most expensive cloud deployment option. This is due to the significant capital investment required for hardware and data center space, especially if colocated.
Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid Cloud environments are becoming an extremely popular type of cloud deployment found in today’s cloud strategies. In the hybrid cloud deployment, your business may decide to blend both the private and public cloud deployments and have a hybrid mix of the two.
In a hybrid cloud deployment, a portion of your data is migrated to a public cloud environment. This data then becomes accessible through the public cloud infrastructure. Meanwhile, other data and systems, which may necessitate more stringent security protocols, are kept in a private cloud. The private cloud may be housed on-premises or collocated in another data center.
A hybrid cloud is a popular option of seeing wide adoption due to the flexibility to decide where certain data is housed. Your business can leverage the power and flexibility of public cloud resources while using private cloud resources for secure access to more sensitive systems.
Multi-Cloud
Another option that may fit in your cloud strategy is Multi-Cloud. A multi-cloud strategy is one where “multiple” public cloud environments may be used to house various business-critical systems. Each public cloud vendor may have certain strengths that can be leveraged to the advantage of your business. For example, Microsoft Azure can offer licensing and other benefits to enterprise environments that are primarily “Microsoft Windows shops.”
The multi-cloud strategy can allow using the best aspects of multiple cloud vendors and helps to minimize “vendor lock-in.” However, multi-cloud deployments can introduce additional complexity. Different public cloud vendors often have unique ways of interacting with their systems. This can result in the need for specific tooling and solutions for each public cloud employed in the multi-cloud approach.
3. Choose a Reliable Cloud Provider
Choosing your cloud provider can be a key aspect of your cloud strategy. This can be a very complex question to answer and will likely be a different answer for each business. However, like forming your cloud strategy, reviewing a potential cloud provider based on important questions can help make the decision. The following questions can help you choose a cloud provider:
- Which cloud provider aligns best with your business?
- Which cloud provider services or features would best help to solve current business challenges?
- Do they have features or solutions potentially on their roadmap that would greatly benefit your business?
- What are their Service Level Agreements?
- What security standards and solutions do they have in place to protect data?
- What about data governance and regulatory solutions built into their platform?
- What is their track record of reliability and performance?
- Do they provide migration support, tools, and solutions to get data in and out of their platform?
A cloud provider that is right for one business may not be right for another. You must scrutinize each cloud provider in terms of your specific business needs and how their solutions and services can help to solve real business challenges.
Risks of a Poor Cloud Strategy
A lack of a definite strategy often leads to unorganized efforts to migrate data. This can result in disparate pieces of data and services being housed in different cloud environments without rhyme or reason. Learn more about cloud data security best practices.
This can lead to data silos and a lack of a cohesive data structure for your cloud resources. It is also important to make sure that cloud POC environments are very structured and monitored. Migrations to the cloud often start with small POC environments of cloud environments and services. Without an official strategy to migrate data, a POC of a cloud environment can quickly turn into a “production” environment with unintended consequences to business continuity.
A poorly architected cloud strategy can have serious security implications, underlining the importance of implementing robust cloud security solutions. Without proper security planning, data can accidentally be exposed to unauthorized internal end-users as well as the outside world.
What about compliance and regulations? It is extremely important, as is the case with GDPR, to think about “where” your data is housed and in which data centers. Without a proper cloud strategy, data could be housed incorrectly or improperly in relation to compliance guidelines. This can result in serious fines and other consequences.
Poorly thought out cloud strategies can also lead to:
- Unintentional oversights of fundamental processes that need to exist in the cloud (i.e., backups of data and others)
- Data is moved haphazardly with no real solution in place to protect the data once it is stored in a cloud environment
- Losing business-critical data and having severe impacts on business continuity.
Asking the right questions is key. It allows you to determine the cloud deployment option that is most suitable for your business. Next, choose the appropriate cloud provider. Keep in mind important cloud considerations such as security and backups. Following these steps, you can develop an effective cloud strategy. This will allow taking full advantage of the cloud and having access to the features and services you need for your business.
Was this helpful?
How Can You Maximize SaaS Security Benefits?
Let's get started with a live demo
Latest blog posts
How to Restore A Backup From Google Drive: A Step-by-Step Guide
April 10, 2024Backing up your Google Drive is like making a safety net for the digital part... Read more
Protecting Partner Margins: An Inside Look at the New Spin.AI Partn...
April 2, 2024Google recently announced a 40% reduction in the partner margin for Google Workspace renewals –... Read more
Expert Insights: SaaS Application Data Protection Fundamentals
March 21, 2024SaaS applications appeal to organizations because they make running the application “somebody else’s problem.” However,... Read more


