Cyber Security Roles and Responsibilities in the Enterprise [2023]

IT security is one of the most fast-paced industries in the world. An estimation shows that there will be 3.5 million unfilled cybersecurity jobs by 2021. There is clearly a demand for skilled security professionals. So let’s take a look at some of the most common cyber security roles and what it takes to fit into them.
Enterprise Cyber Security Roles and Responsibilities
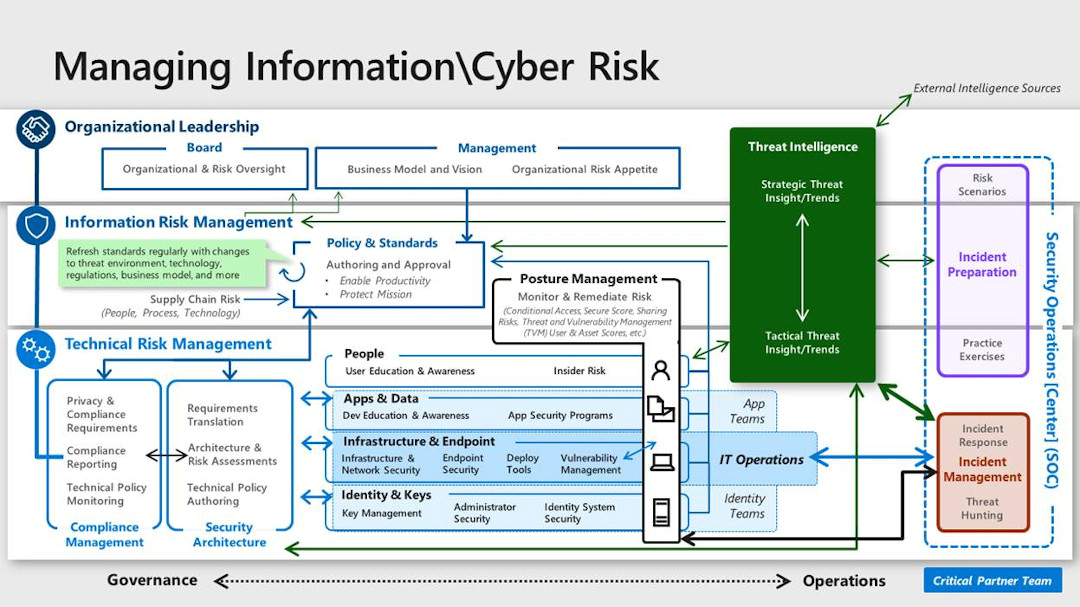
Source: Microsoft
Here are some of the vital IT security roles and the responsibilities associated with them. Don’t be surprised that sometimes, different roles share some responsibilities. After all, cybersecurity requires a complex approach from professionals working in this field.
Application Security Engineer
The job of an app security engineer has two major aspects. Firstly, you will need to help developers to create more secure apps. Secondly, you’ll need to control third-party apps used by your company and ensure their safety. Some of the typical responsibilities and tasks include:
- Configuring technical security controls
- Conducting an application risk assessment
- Whitelisting/blacklisting apps
- Performing penetration testing
For app security engineers, it’s vital to control SaaS apps and the risks related to them. Risky and insecure apps should be blacklisted. To automate your job and remain time-efficient, you’ll probably need specialized software that helps you with SaaS application risk assessment and whitelisting/blacklisting.
CISO
A CISO (Chief Information Security Officer) is a C-level employee whose task is to oversee corporate security strategy. The typical CISO’s responsibilities include:
- Planning long-term security strategy
- Planning and implementing data loss prevention measures
- Managing access to enterprise assets
- Ensuring that the company implements proper safeguards to meet compliance requirements
- Investigating any incidents and preventing them in the future
- Assessing security risk
- Arranging security awareness training
Data Protection Officer
Having a DPO is one of the GDPR compliance requirements. A DPO must be appointed in organizations working with large-scale systematic monitoring or processing of sensitive data. Officers oversee corporate data protection measures and their effectiveness. A specialist, appointed to the DPO role, controls whether corporate security is of a sufficient level to meet compliance requirements, and recommends security upgrades if needed. That’s why an in-depth understanding of data security and compliance are essential skills. You can read more about the role of DPO here.
Network Security Engineer
As the name suggests, a network security engineer’s job is to protect corporate networks from data breaches, human error, or cyberattacks. Engineers are responsible for:
- Configuring network security settings
- Performing penetration testing
- Developing and implementing sufficient measures to detect cyber security threats
- Implementing network security policies
- Installing and maintaining security software like firewalls or backups.
Also, a deep understanding of cloud security may be required.
Security Administrator
An IT security admin is a role that includes a wide range of skills and responsibilities to manage the protection of the company’s data. Some of the most common admin’s responsibilities include:
- Managing access
- Ensuring that data migration is secure
- Configuring security software
- Monitoring data behavior for abnormal activities
- Implementing security policies
- Testing company’s systems to locate potential risks and vulnerabilities
- Reporting security statuses and incidents (if any)
- Using software tools to automate some of the tasks
An admin’s role is more significant than it may seem at first glance. An admin has to keep the whole organization’s security landscape in mind and ensure that even the tiniest processes are executed correctly. After all, even one careless click may be enough to initiate a cyberattack.
Security Analyst
What is the role of an information security analyst? This role is related to protecting corporate information against cyberattacks and insider threats. Generally, an analyst has to determine potential risks and vulnerabilities inside the system, so a deep understanding of data security threats and ways to prevent them is a must. As a security analyst, your responsibilities will include:
- Analyzing and configuring corporate systems to improve their security
- Analyzing data loss prevention measures
- Looking for system vulnerabilities and ways to fix them
- Monitoring data behavior for abnormal activities
- Verifying security, availability, and confidentiality of corporate data
Also, the security analyst’s role requires an understanding of white hat hacking to design more advanced protection against cyberattacks. Analysts often work together with security architects.
Security Architect
A security architect is one of the senior-level IT security positions. An architect is focused on creating a secure-by-design environment. Unsurprisingly, this position requires a solid understanding of network, app, and hardware security, as well as experience with various systems. Generally, an architect’s responsibilities include:
- Assessing the system’s security controls and processes to find potential security gaps
- Planning changes and upgrades for corporate IT infrastructure
- Maintaining system integrity
- Implementing insider threat control measures
- Choosing new security software if needed
- Implementing disaster recovery measures
- Analyzing previous incidents and creating an incident response plan
- Analyzing the costs and benefits of security solutions
Of course, the exact scope of your tasks as an architect will vary depending on each organization’s unique infrastructure and needs. Often, an architect needs to assess corporate systems for meeting security compliance standards like HIPAA or NIST to decide what changes are needed to become compliant.
Security Specialist
An IT security specialist is a person responsible for keeping corporate data safe. Security specialists maintain and upgrade systems and procedures to prevent data loss or leakage. IT specialists have many sub-specializations. Depending on a specific environment, an information security specialist will have a stronger focus on cloud, network, app, database, SCADA, or device security. In some cases, especially in small businesses, an IT security specialist is an all-rounder with responsibilities combining many cybersecurity roles at the same time. That’s why a security specialist must have strong IT skills and a deep understanding of both software and hardware—and, of course, an ability to locate potential vulnerabilities and fix them.
Protecting Remote Work
Cybersecurity roles and responsibilities are related not just to a fixed skillset, but also to a complex vision of the cybersecurity landscape. Besides, malicious software and cybersecurity tools are evolving constantly, and being up-to-date is essential for protecting your company’s data. As the coronavirus outbreak spreads throughout the world, many working environments are becoming fully or partially remote. IT security professionals should lead the change and ensure the security of remote work. And that’s how.
SaaS Security Posture Management by Spin One
SpinOne is a next-generation cloud SaaS Security Posture Management (SSPM) solution that leverages the capabilities of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to provide an automated enterprise security solution. It offers organizations the following capabilities:
- It provides the ability to fix shared mailboxes and files that are easy targets for hackers (Microsoft even recommends blocking sign-ins for shared mailbox accounts)
- Cloud Data Access Control for internal and external users – know who is accessing business-critical data, both from within and outside the organization
- Easily offboard employees, including taking ownership of user account data by an admin, blocking access, migrating data to another cloud SaaS user account
- Applications Risk Assessment – Maximize control and visibility in cloud SaaS applications where security gaps exist or may arise. Spin allows taking control of the applications users can access and integrate with cloud SaaS environments
- Enhanced visibility into applications used within the organization and allows to act immediately to fix any gaps to prevent data breaches and to put in place measures that ensure you maintain complete control over your data. This capability ensures no data subsets are anonymously accessible.
- Automated Ransomware Protection – SpinOne provides automated ransomware protection that detects ransomware attacking your cloud SaaS data, blocks access to the malicious process, identifies affected files, and automatically restores data affected by the attack.
Reducing the security cost and security management effort
Today the threats against business-critical data are ominous. As organizations struggle with the current challenges of the hybrid workforce, they cannot neglect their security posture. SaaS Security Posture Management (SSPM) solutions provide today’s businesses with the automated tools needed to combat modern threats. The responsibility of configuring cloud SaaS applications for top-level security lies with the business, not the cloud service provider. To reduce the security cost and security management effort, utilizing SSPM solutions reduces the overall risk from a security perspective and bolsters its effectiveness. SpinOne’s automated security features help reduce the cost, time, and effort for in-house security teams struggling to keep up with escalating risks and multiple cloud SaaS applications.
Cybersecurity profession
In this section, we’ll discuss cybersecurity profession and its current challenges.
What is enterprise cybersecurity and who are cybersecurity professionals?
Enterprise cybersecurity is the body of strategies, practices, and tools to ensure the security of corporate data and protect corporate IT systems from malicious cyber incidents.
With the YoY increase in cybercrime, the importance of cyber security in modern enterprise is becoming critical. As a result, we see the growing need for cybersecurity professionals.
A cybersecurity professional is a person with skills that match one or several cybersecurity roles. This job requires a higher education degree, work experience, and skills. The cybersecurity landscape is very dynamic. That’s why people who chose this line of work will have to constantly monitor the new strategies and know the best practices for cyber security professionals.
Challenges Faced by Cyber Security Professionals
Modern cybersecurity professionals face multiple challenges in their day-to-day work. There are three main factors that influence the work of cybersecurity teams across the globe:
- The adoption of the cloud.
- The surge of cybercrime.
- The rapid change in technology.
The cloud adoption ruined the security architecture as we knew it back in the 2000s and early 2010s when the company had an on-prem system with perimeter security. Previously to access the corporate system, a user needed to be physically present in an office, which enabled security teams to create an additional layer of security.
When it comes to the cloud, anyone can access it using an Internet connection from any point in the world. Furthermore, other applications can access your cloud systems using OAuth. It creates a greater attack surface that is hard to control for an IT team.
The global accessibility of IT systems partially contributed to the surge of cybercrime. It is an easy way of income with little to no ability to find out who the criminal is. The surging crime boosted the response from the cybersecurity tools market, which in its turn forced cybercriminals to search for new ways to infiltrate the IT system. Basically, we see the constant arms race happening right here and right now.
These processes impact cybersecurity professionals in a detrimental way. First, they constantly face overload with the necessity to defend against a large attack surface of the cloud IT systems. Second, they work under the constant pressure of cybercrime and the rapid change of attack methods and technology that combats attacks.
As a result, cyber professionals face the following challenges:
- Stress due to the constant work overload.
- Talent gap as a sizable percentage of experts leave the profession while the need to increase the number of security team members grows.
- Skill gap due to the technology arms race.
FAQ
What are the key cyber security roles typically found in an organization?
The key cybersecurity roles found in an organization are Network Security Engineer, Security Administrator, Application Security Engineer, Security Analyst, CISO, Security Architect, and Security Specialist.
What does a Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) do, and why is this role crucial?
CISO is usually responsible for long-term planning and security strategy, as well as supervising compliance and access, assessing security risks, investigating incidents, and arranging training. CSIO usually orchestrates enterprise cybersecurity and is crucial for multiple processes within the company.
How do Security Analysts contribute to an organization’s cybersecurity defense?
Security Analysts are responsible for protecting corporate data from potential threats and attacks by identifying risks and vulnerabilities in the system.
What responsibilities do Network Security Engineers have in securing an enterprise’s network infrastructure?
Network Security Engineers protect corporate networks from data breaches and other cyber incidents by configuring network settings, pen-testing, and implementing security policies.
How can Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies enhance cyber security efforts?
AI and ML technologies can help cybersecurity teams by decreasing the workload as well as processing large data pools, and detecting abnormalities.
Was this helpful?
How Can You Maximize SaaS Security Benefits?
Let's get started with a live demo
Latest blog posts
How to Restore A Backup From Google Drive: A Step-by-Step Guide
April 10, 2024Backing up your Google Drive is like making a safety net for the digital part... Read more
Protecting Partner Margins: An Inside Look at the New Spin.AI Partn...
April 2, 2024Google recently announced a 40% reduction in the partner margin for Google Workspace renewals –... Read more
Expert Insights: SaaS Application Data Protection Fundamentals
March 21, 2024SaaS applications appeal to organizations because they make running the application “somebody else’s problem.” However,... Read more


